What is acupuncture?
Why choose acupuncture?

What does acupuncture actually do?
* Acupuncture increases the release of endorphins, substances that inhibit pain.
* Acupuncture stimulates and regulates the endocrine system.
* Acupuncture enhances the body's immune function.
* Acupuncture increases the body's circulation.
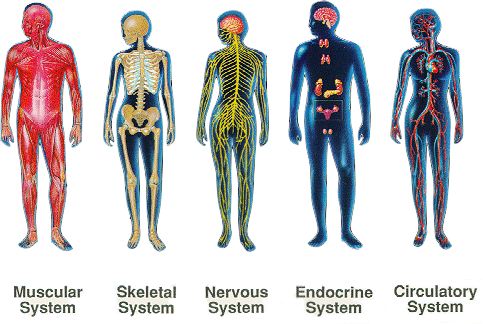
How does acupuncture work?
2. Autonomic Nervous System Theory: Acupuncture stimulates the release of norepinephrine, acetylcholine and several other types of opioids, affecting changes in their turnover rate, normalizing the autonomic system, and reducing pain. 10, 11
3. Vascular-interstitial Theory: Acupuncture effects the electrical system of the body by creating or enhancing closed-circuit transport in tissues. This facilitates healing by allowing the transfer of material and electrical energy between normal and injured tissues. 9
4. Blood Chemistry Theory: Acupuncture affects the blood concentration of triglycerides, cholesterol, and phospholipids, suggesting that acupuncture can both raise and diminish peripheral blood components, thereby regulating the body toward homeostasis. 9
5. Gate Control Theory: Acupuncture activates non-nociceptive receptors that inhibit the transmission of nociceptive signals in the dorsal horn, "gating out" painful stimuli. 11
- 1. “A review of the incorporation of complementary and alternative medicine by mainstream physicians”, Astin, JA., et. al., Arch Intern Med., 1998; (158).
- 2. The Institute for Work & Health, “Massage for Lower Back Pain”, Spine, 2009, July 15: 34 (16).
- 3. “German Acupuncture Trials (GERAC) for Chronic Lower Back Pain”, Archives of Internal Medicine, 2007; 167(17).
- 4. Department of Medicine and Health Sciences, “Acupuncture Just as Effective Without Needle Puncture”, Science Daily, December 1, 2008, study conducted by the at Linkoping University and the Vardal Institute in Sweden.
- 5. “Effects of Acupuncture of Pregnancy and Live Births Among Women Undergoing In Vitro Fertilization: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis”, British Medical Journal, 2008: 336: 545, published February 7, 2008.
- 6. “Immunomodulatory Effects of Acupuncture in the Treatment of Allergic Asthma: A Randomized Controlled Study”, The Journal of Alternative and Complementary Medicine, Vol 6, Issue 6, 2007.
- 7. Neuro-acupuncture, “Scientific evidence of acupuncture revealed”, Cho, ZH., et al., 2001.
- 8. Acupuncture – A scientific appraisal, Ernst, E., White, A., 1999, p. 74.
- 9. Acupuncture Energetics, “A Clinical Approach for Physicians”, Helms, Dr. J., 1997, pgs 41-42, 66.
- 10. National Institute of Health Consensus Conference on Acupuncture, “Acupuncture Activates Endogenous Systems of
- Analgesia.”, Han, J.S., 1997 (Bethesda, MD).
- 11. Neuro-acupuncture, “Scientific Evidence of Acupuncture Revealed”, Cho, ZH., et al., p.116.
What conditions can acupuncture treat?
• Acne
• Anxiety
• Arthritis
• Asthma
• Autoimmune Disease
• Bronchitis
• Cancer Pain
• Carpal Tunnel Syndrome
• Chronic Fatigue
• Colitis
• Common Cold
• Constipation
• Crohn’s Disease
• Dental Pain
• Diarrhea
• Dizziness
• Dysmenorrhea
• Emotional Problems
• Endometriosis
• Facial Palsy
• Fatigue
• Fertility
• Fibromyalgia
• Headache
• Hiccough
• Hormonal Imbalance
• Incontinence
• Indigestion
• Insomnia
• IBS
• Low Back Pain
• Menopause
• Menstrual Issues
• Migraine
• Morning Sickness
• Nausea
• Neuropathy
• Neurological Disorders
• PMS
• Pneumonia
• Postoperative Recovery
• PCOS
• Reproductive Care
• Rhinitis
• Sciatica
• Shingles
• Shoulder Pain
• Sinusitis
• Sleep Disturbances
• Smoking Cessation
• Sore Throat
• Stress
• Thyroid Disorders
• Tonsillitis
• Trigeminal Neuralgia
• Vomiting
• Weight Management
Is acupuncture safe?
Does acupuncture hurt?
Size comparison

What if you don't like needles?
How many treatments will you need?
What is Chinese herbal medicine?


What are herbal medicines made out of?
What forms of payment are accepted?
Cash, check, or credit card all acceptable forms of payment.
Do you accept insurance?
Yes, currently we are in-network with HealthPartners insurance only.
Patients with HealthPartners insurance should be aware about what health conditions are potentially covered.
* If you do not have Health Partners Insurance, then we can provide you with a medical superbill, which you can then submit to your insurance for reimbursement purposes.
